Patent fundamentals
A comprehensive guide to the fundamentals of patents and patenting in Australia and internationally
DEFINITION
What is a patent?
A patent is a type of intellectual property that is issued by a government and gives its owner the right to stop others making, using, selling and importing versions of a new product and/or process.
IDEA OR INVENTION?
Can you patent an idea?
If the idea is a new product or process that has practical advantages, we call it an invention and there’s a good chance that it’s patentable. The invention will need to satisfy the patentability requirements discussed below, but they are not as challenging as you might imagine.
APPLICATION PROCESS
How to patent an idea
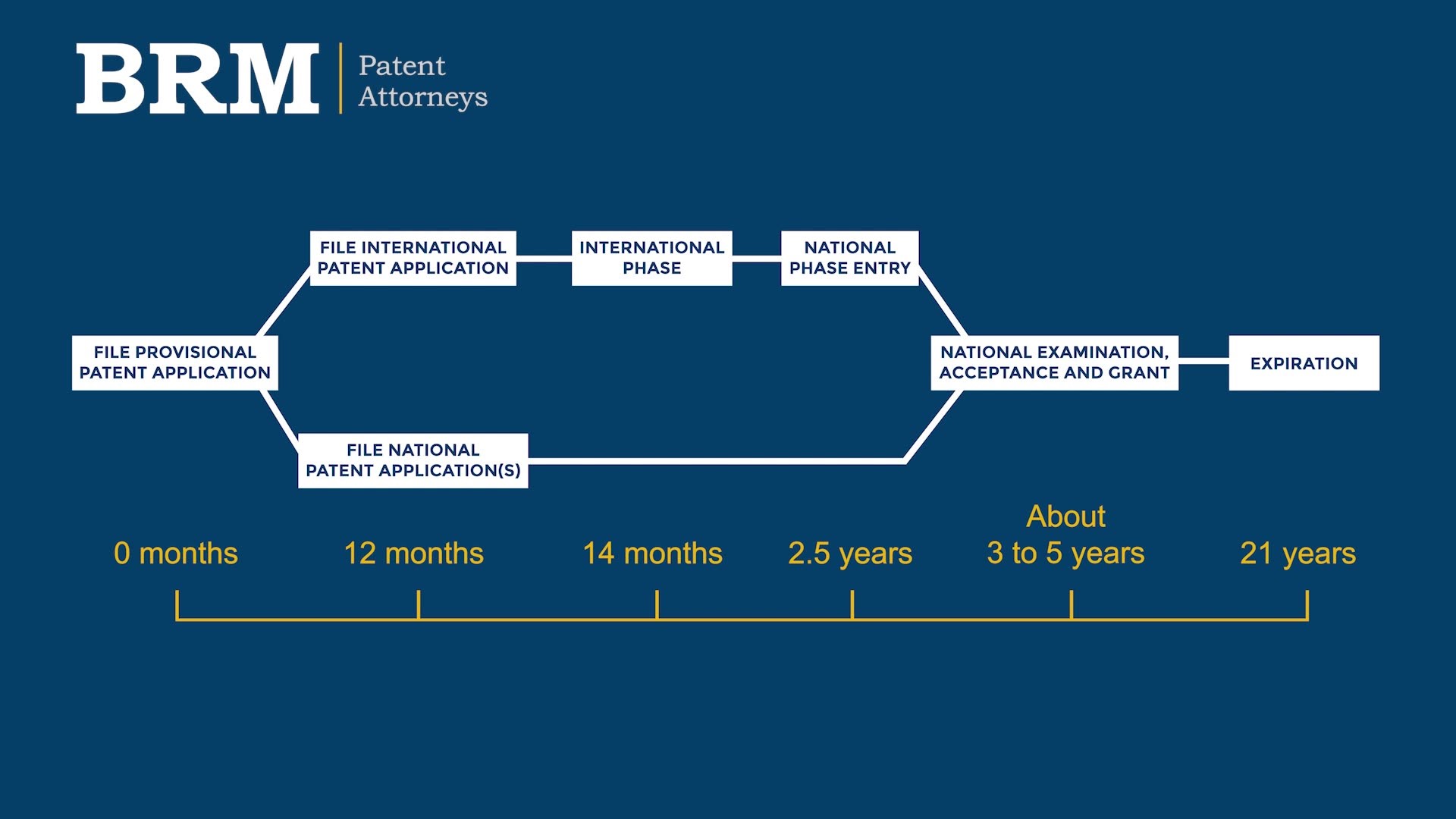
The process often starts with a provisional patent application followed by one or more non-provisional patent application(s) about 12 months later. The non-provisional application(s) will then be examined to check that the invention qualifies. A patent is usually granted shortly after an application passes examination. more
COST
How much does a patent cost?
Securing an Australian patent often costs about $17,000 + GST over about four or five years. International strategies often cost about $100,000 + GST over the first four years, e.g. if you aim to cover several individual countries plus Europe as a region. more
BENEFIT
Why file a patent?
- To preserve profit margin by limiting competition.
- To generate new income streams by licensing.
- To demonstrate to the market that you are innovative.
- To attract investors.
- To foster an innovative business culture.
ASSIGNING PATENTS
Can you sell a patent?
Yes – patents are commercial assets that can be bought, sold and assigned like other assets. They can also be licensed to generate royalty streams.
QUALIFYING FOR PROTECTION
Patentability requirements
The key requirements for a valid patent are novelty, an inventive step and inherent patentability. The invention must also be useful, so ‘inventions’ that don’t work (such as perpetual motion machines) can’t be validly patented, and the text and figures of the patent must:
- include claims that define the invention (that is, define the patent coverage) and are clear* and succinct*;
- sufficiently describe the invention to enable it to be implemented without the need for invention or undue burden; and
- support (or justify) the scope of the claims.
* Well, in theory they must be clear and succinct – in practice, very few Australian patent claims are held invalid because they are unclear and/or verbose.
DEFINITIONS OF COVERAGE
Patent claims
The coverage of a patent is defined by its ‘claims’. Myths such as ‘a 10% change avoids patent infringement‘ are not helpful.
The wording of the claims is critical. Each claim is a single sentence that can be thought of as a list of features. Generally speaking, to infringe a patent claim, each and every feature of the claim must be taken.
Example patent claim
A plumbing fitting including:
- an inlet conduit;
- a first outlet conduit;
- a second outlet conduit;
- a valve for closing the first outlet conduit; and
- a solenoid valve for closing the second outlet conduit.
Plumbing fittings which do not include a solenoid valve for closing the second conduit are not covered by this claim. Infringement could be avoided by substituting another type of valve for the solenoid valve.
On the other hand:
- the claim simply specifies ‘a valve for closing the first outlet conduit’ – a plumbing fitting including any type of valve for closing the first outlet conduit is covered; and
- the claim is silent on the inlet conduit having a valve, so the claim covers plumbing fittings with or without a valve on the inlet conduit.
A patent will typically include multiple claims of differing scope. To successfully enforce a patent, only one claim need be valid and infringed.
The approach to claim interpretation varies from country to country. In Australia, claim wording must be interpreted from the point of view of an individual familiar with the relevant field of technology, and be given its plain and ordinary meaning in the context of the patent read as whole. Some countries, most notably the US, have rules which vary the scope of coverage relative to the plain meaning of the claim wording.
NEW AND NON-OBVIOUS
Novelty and inventive step
To qualify for a patent, an invention must be novel (strictly new) and have an inventive step. An inventive step requires ‘non-obviousness’ – that is, something more than a routine development in the technology or a plain and logical extension of what is already publicly known. Synergies and surprising and unexpected results are indicators of an inventive step.
MANNER OF MANUFACTURE
Inherent patentability – patentable subject matter
Beyond novelty and an inventive step, the invention must also be inherently patentable to qualify for a patent. This is a notoriously difficult topic. It attempts to separate patentable technical innovation from inherently unpatentable abstract ideas, business innovation, artistic works and mere discoveries.
Fortunately, many new ideas are far removed from this difficulty. Typically, three-dimensional products (and physical processes) that offer some technical benefit clearly meet the inherently-patentable standard.
There has been much controversy regarding the patentability of certain classes of software whereas, generally speaking, software that implements a new technical solution to a technical problem remains uncontroversially patentable, e.g. the New Zealand Patent Office gives the example of a patentable software upgrade to a washing machine (here).
Likewise, abstract ideas such as a mathematical algorithm without practical application aren’t patentable, but a new machine that uses the algorithm for some practical purpose could be.
Inherent patentability is a complex topic that cannot be reduced to a simple definition. In Australia, an invention must be a ‘manner of manufacture’. The concept is rooted in 400 years of case law that indicate that the wording ‘manner of manufacture’ is merely a ‘general title’ for the principles developed in the case law.
Fortunately, for the atypical cases that might not be inherently patentable, the Australian, US and European Patent Offices provide many pages of guidance on the topic (here, here and here) and we’re always happy to chat. Contact Us.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE GENERAL RULE
Grace periods
So long as patenting remains of interest, it’s important to:
- keep the invention secret; and
- ensure that examples of the invention are not sold or commercially used (even under the cover of a confidentiality agreement / non-disclosure agreement)
until a quality patent application is filed.
As a general rule, a patent cannot validly cover anything that was publicly known before its ‘priority date’. ‘Publicly known’ takes in everything that is not secret. The ‘priority date’ is the filing date of the first effective patent application.
Twelve-month grace periods available in Australia, New Zealand, the US, Canada and a few other countries are exceptions to this general rule. These grace periods enable you to start a valid patent strategy after you have published relevant information.
The grace periods should be viewed as backups, rather than relied on as a matter of course:
- most jurisdictions do not have general grace periods; and
- even in the few grace period countries, valid patents won’t be possible if others independently go public with relevant technology before your first patent application is filed.
CAN YOU PATENT AN IDEA WITHOUT A PROTOTYPE?
When should you file a patent application?
Usually, it’s best to file as soon as you are confident that the invention works and there is a business case for patenting.
There’s no need for a prototype, but if you’re at a very early stage and there are still real technical challenges to make the invention work, it might be too early to file an effective patent application.

For a patent application to be effective it must include ‘enabling detail’ that teaches the ‘ordinary non-inventive worker’ in the relevant industry how to make and use the invention without undue burden.
Filing an effective patent application sets the ‘priority date’ for the invention. This is the key date used to assess whether your invention satisfies the novelty and inventive step tests. Filing sooner to set an earlier priority date improves the prospects of passing those tests: if you defer filing a patent application whilst you make refinements, you might miss out if similar technology is published in the meantime.
A provisional patent application can be filed to set a priority date for the initial detail and open a 12-month window to file a non-provisional patent application that captures, and sets a priority date for, any technical refinements in the meantime. More on How to patent an idea.
DESIGN & UTILITY PATENTS
Types of patents
There are two types of patent in Australia: standard patents which last for 20 years and innovation patents which last for 8 years and are being phased out.
The wording is used differently in the USA. There are three types of patent in the USA – utility, design and plant.
US utility patents protect technical innovation and are examples of ‘patents’ as the word is used in Australia, most other places and on this page.
US design patents protect the appearance of products whereas Australia has design registrations.
US plant patents protect plant varieties whereas Australia has plant breeder’s rights.
Provisional and PCT patents (strictly speaking, provisional and PCT patent applications) are discussed below.
RESERVE YOUR PLACE
What is a provisional patent application?
A provisional patent application is a place-marker that reserves your priority to patent an invention.
The filing date of an adequate provisional patent application is called the ‘priority date’. That’s the key date that patent examiners will use when assessing whether your invention qualifies for a patent. Generally speaking, a patent cannot validly cover anything that was publicly known before its priority date, although some countries have grace periods. more
PCT APPLICATIONS
What is the Patent Cooperation Treaty?
The PCT is an international agreement by which most countries each agree to treat a single international patent application as a local national patent application. PCT applications currently cover 157 countries:
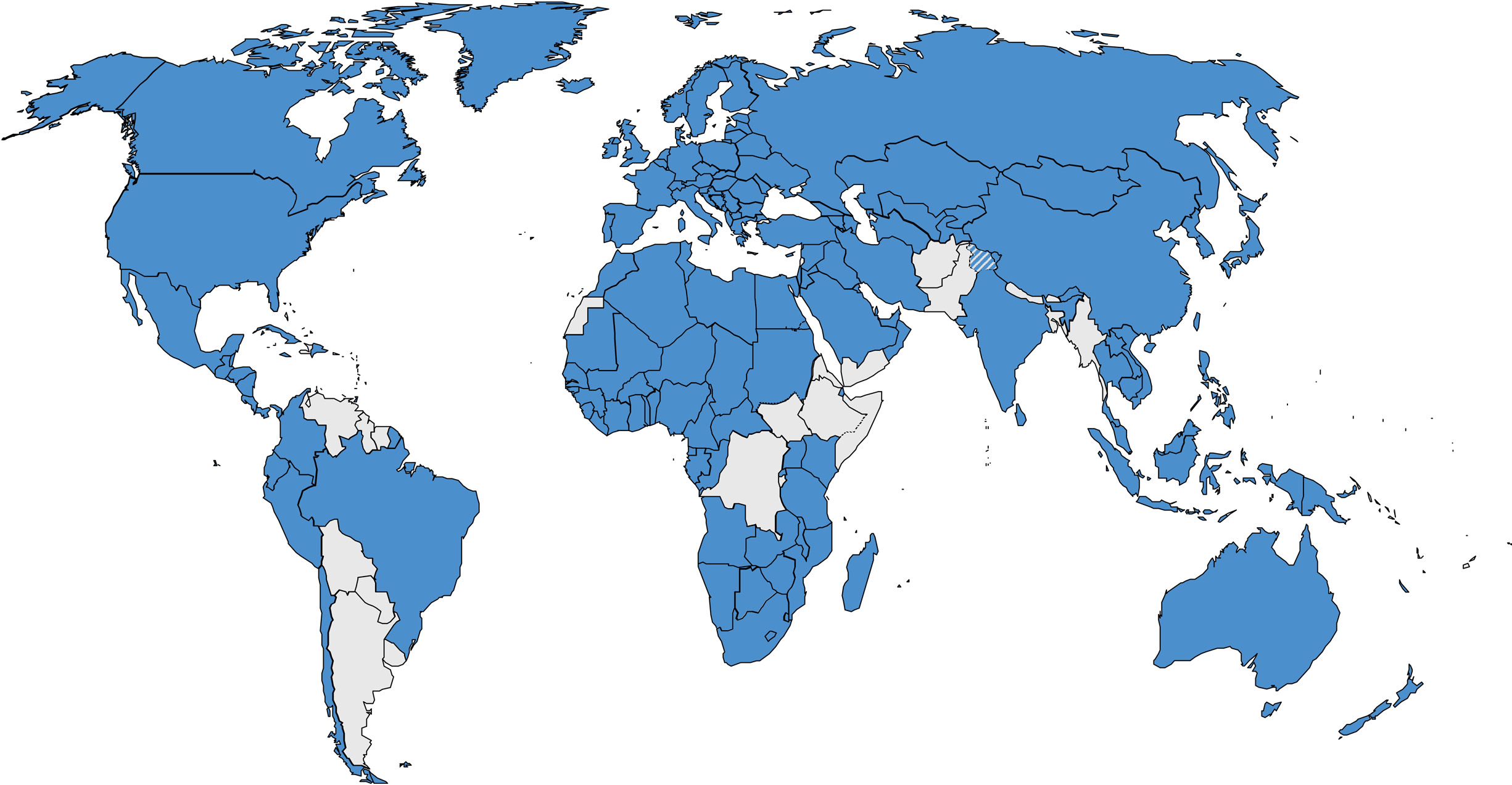
Source: World Intellectual Property Organization
A PCT application is a good option if you’re aiming to patent in multiple countries. It defers the separate country by country processes and costs by up to 2.5 years. more
GRANTED COUNTRY BY COUNTRY
National patents
Generally speaking, patents are granted country by country but are not defeated simply by manufacturing in other countries.
An Australian patent covering a product would be infringed by:
- importation into Australia;
- sale in Australia; and/or
- use in Australia
without the patentee’s permission, regardless of where the product is made.
Additionally, an Australian patent covering a method would be infringed by doing any of those things (e.g. importing, selling and/or using) in connection with a product resulting from a version of the method.
THE RIGHT TO EXCLUDE
Exclusive right to make, use, sell, import and more
Strictly speaking, an Australian patent gives its owner the ‘exclusive right’ to ‘exploit’ the invention:
“exploit, in relation to an invention, includes:
(a) where the invention is a product—make, hire, sell or otherwise dispose of the product, offer to make, sell, hire or otherwise dispose of it, use or import it, or keep it for the purpose of doing any of those things; or
(b) where the invention is a method or process—use the method or process or do any act mentioned in paragraph (a) in respect of a product resulting from such use.”
More practically, an Australian patent gives its owner the right to stop others from exploiting the invention.
Patent rights are exclusive rights, as in the right to exclude others from making, using, selling and/or importing versions of the invention. Patents do not give their owners the right to make, use, sell and import versions of the invention.
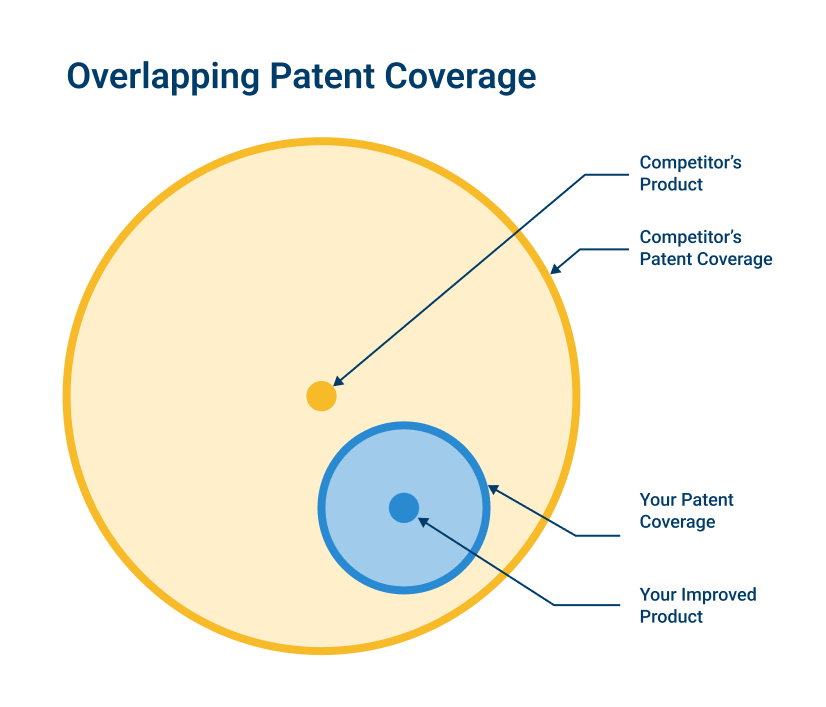
Imagine:
- your competitor has a patented product;
- you see room for improvement; and
- you patent the improved version.
It could well be that your patent and the competitor’s original patent both cover the improved version and neither of you are allowed to make the improved version unless you and your competitor co-operate.
PATENT TERM
How long does a patent last?
20 years is the standard patent term in Australia, the US and most other countries. The 20-year term is usually calculated from the filing date of the first non-provisional patent, so an additional 12 months of protection can be secured by filing a provisional patent application. more
PATENT PENDING
What does ‘patent pending’ mean?
Patent pending’ means a patent has been applied for. Once patent has been granted, products and/or processes covered by the patent can be marked and marketed as ‘patented’.
PUT THE IMITATORS ON NOTICE
Patent markings
Marking products and/or processes with ‘patent pending’ or ‘patented’, or (better yet) the patent application numbers and patent numbers, puts potential infringers on notice of the patent rights to improve the prospects of recovering damages for infringement.
Virtual marking (VM) is an alternative to conventional marking and is usually the better option, in our view.
Conventional marking – Markings such as ‘Patent pending’ and ‘AU patent application no. 2018123456’ have long been applied to products, packaging and/or marketing materials. These markings might be embossed on the product or printed on the packaging. Such markings are still appropriate, particularly in very simple cases (e.g. in relation to a single patent for a single product in a single country).
Typically, the appropriate markings will change from time to time, such as when a patent is granted on a patent application or when a patent ceases. It is important to keep the markings up to date. Falsely marking a product as patented is an offence. Updating conventional markings can be costly, e.g. if packaging has to be replaced.
Virtual Marking (VM) minimises the cost of updating the markings. VM entails:
- maintaining a webpage listing the products and/or processes and the corresponding patent rights;
- maintaining a credible record of what the webpage looks like from time to time; and
- marking products, packaging and/or marketing materials with a reference to a webpage, e.g. ‘patents applied for – see www.mywebpage.com.au/patents’.
VM is officially recognised in the United States. Whilst the position is not as clear elsewhere, virtual marking is usually the better option, in our view.
VIOLATION & BREACHES
Patent infringement
A patent is infringed by making, using and/or selling a relevant product and/or process covered by the patent, without the patent owner’s permission. The penalties for patent infringement can include an ‘injunction’ to stop the infringing action (e.g. to stop the making, using, selling and/or importing of an infringing product) and significant financial penalties. more
RESPONDING TO INFRINGEMENT
Patent enforcement
If you believe that your patent is being infringed, it is important to verify that the patent validly covers the infringing product before reaching out to the infringer. Reaching out with professionally prepared correspondence improves the prospects of success. If the dispute cannot be resolved through correspondence and/or mediation (etc), patents are enforced in the courts. more
OTHER TYPES OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
Alternatives to patents
Patents are not the only options for guarding against imitators. Design registrations can be used to stop others copying the appearance of new products. Some technologies such as ‘in house’ methods can be kept as trade secrets, but trade secrets do not protect you from reverse engineering or from your competitors independently developing similar technology. more
PATENT LORE
Patent myths
LAWYER V ATTORNEY
What is a patent attorney?
Patent attorneys are specialists who secure and advise on the coverage of patents. Australian patent attorneys have both technical and legal training and are registered with the Trans-Tasman IP Attorneys Board. Patent lawyers are lawyers with particular expertise in enforcing, challenging and/or licensing patents, etc. more


