What is a patent?
A patent is a form of intellectual property that gives its owner the right to stop others making, using, selling and/or importing versions of an invention. Patents are granted by governments, usually country by country, and typically last for 20 to 21 years.
EXCLUSIVE RIGHT TO EXPLOIT
Exclusive right to make, use, sell, import and more
Strictly speaking, an Australian patent gives its owner the ‘exclusive right’ to ‘exploit’ the invention:
“exploit, in relation to an invention, includes:
(a) where the invention is a product—make, hire, sell or otherwise dispose of the product, offer to make, sell, hire or otherwise dispose of it, use or import it, or keep it for the purpose of doing any of those things; or
(b) where the invention is a method or process—use the method or process or do any act mentioned in paragraph (a) in respect of a product resulting from such use.”
THE RIGHT TO EXCLUDE
No right to make, use, sell and/or import
Patent rights are exclusive rights, as in the right to exclude others from making, using, selling and/or importing versions of the invention. Patents do not give their owners the right to make, use, sell and import versions of the invention.
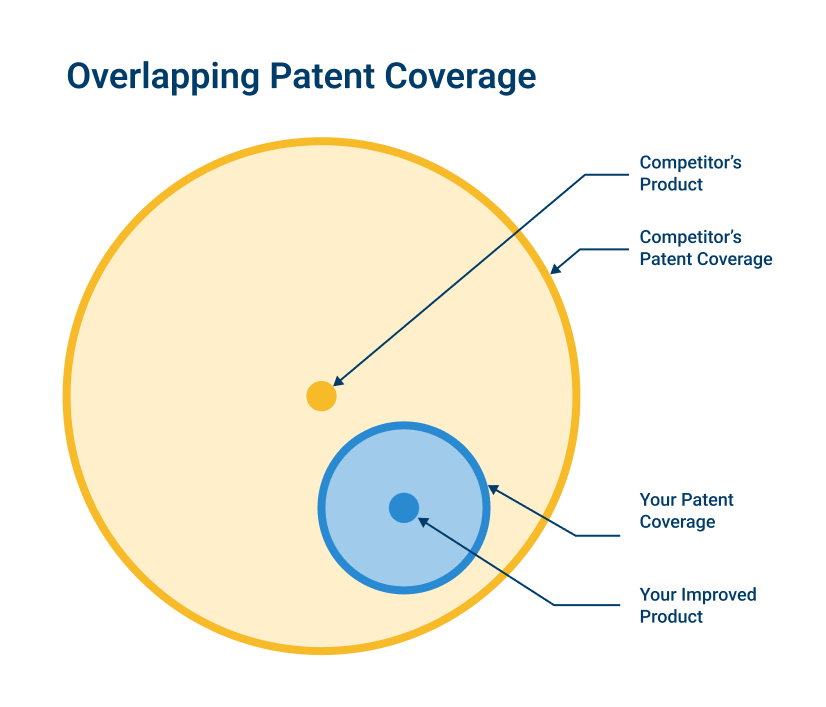
Imagine:
- your competitor has a patented product;
- you see room for improvement; and
- you patent the improved version.
It could well be that your patent and the competitor’s original patent both cover the improved version and neither of you are allowed to make the improved version unless you and your competitor co-operate.
GRANTED COUNTRY BY COUNTRY
Exclusive right to use, sell and import
Generally speaking, patents are granted country by country but are not defeated simply by manufacturing in other countries.
An Australian patent covering a product would be infringed by:
- importation into Australia;
- sale in Australia; and/or
- use in Australia (amongst other things)
without the patentee’s permission, regardless of where the product is made.
Additionally, an Australian patent covering a method would be infringed by doing any of those things (e.g. importing, selling and/or using) in connection with a product resulting from a version of the method.
DESIGN & UTILITY PATENTS
Types of patents
There are two types of patent in Australia: standard patents which last for 20 years and innovation patents which last for 8 years and are being phased out.
The wording is used differently in the USA. There are three types of patent in the USA – utility, design and plant.
US utility patents protect technical innovation and are examples of ‘patents’ as the word is used in Australia, most other places and on this page.
US design patents protect the appearance of products whereas Australia has design registrations.
US plant patents protect plant varieties whereas Australia has plant breeder’s rights.
INVENTION VS IDEA
What is an invention?
An invention is an idea, such as a new product or process, that has practical advantages.
Abstract ideas, such as a mathematical algorithm without practical application, are not patentable. On the other hand, a new machine that uses the algorithm for some practical purpose could be patentable. more
PATENT TERM
How long does a patent last?
20 years is the standard patent term in Australia, the US and most other countries. The 20-year term is usually calculated from the filing date of the first non-provisional patent, so an additional 12 months of protection can be secured by filing a provisional patent application. more
OTHER TYPES OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
Alternatives to patents
Patents are not the only options for guarding against imitators. Design registrations can be used to stop others copying the appearance of new products. Some technologies such as ‘in house’ methods can be kept as trade secrets, but trade secrets do not protect you from reverse engineering or from your competitors independently developing similar technology. more
Further reading